Table of Contents
Vijay Jayaraj
Vijay Jayaraj is a Research Associate at the CO2 Coalition, Arlington, Virginia. He holds a master’s degree in environmental sciences from the University of East Anglia, U.K.
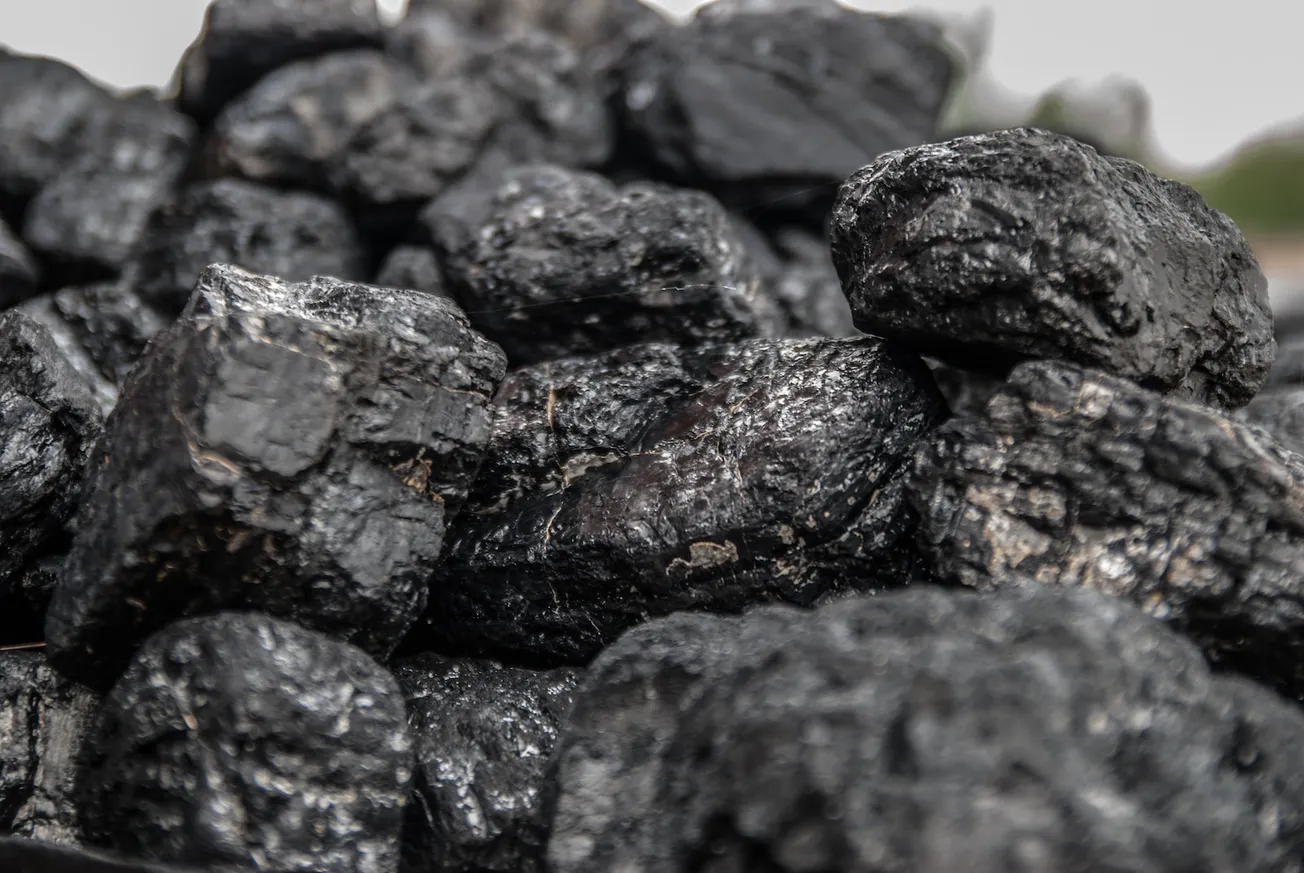
Vietnam and other Asian countries are on a coal spree! Given the dynamics of energy use in the rapidly developing industrial sector there, it is no surprise that these nations have backpedaled on big promises made at international climate conferences to reduce emissions of carbon dioxide from fossil fuels.
Vietnam’s projected 2024 growth rate for Gross Domestic Product (GDP) stands at 5.8%, the sixth highest in Asia. Among the biggest contributors to GDP is the industrial sector (38 percent), especially manufacturing. S&P Global has noted a considerable improvement in Vietnam’s manufacturing sector in the fourth quarter of 2023 and is expecting Vietnam to perform well this year.
Electricity is a cornerstone of manufacturing operations in Vietnam. In 2023, coal produced more than 40% of all electricity in the country, while the country’s abundant hydro reserves contributed around 30%. Natural gas accounted for about 10%.
However, 2024 is expected to see a shortfall in hydroelectric generation because of less rainfall. Simultaneously, electricity production with natural gas is being complicated by forecasts of higher gas prices. Bloomberg reports that state-run PetroVietnam Gas “recently decided not to purchase a cargo for June due to high offer prices.”
So, the heavy lifting to meet power demand must now come from coal. The country is urging coal miners to maximize production before demand reaches peak in the summer months. The country’s prime minister has asked for an increase in coal exploration as well, signaling a sustained interest in the medium to long-time reliance on coal.
Vietnam’s move to increase coal use was inevitable. It cannot continually risk a huge demand-supply gap whenever dams go dry or gas prices skyrocket. The growth rate of power demand from expanding industries is increasing at a fair pace, and energy security is critical in ensuring manufacturing’s positive trend.
Similar patterns across Asia
Across Asia, a similar phenomenon is unfolding. The regional coal resurgence can be attributed to the rapid economic growth in these countries. China, the world’s largest coal consumer, witnessed a rise in consumption in 2024. Earlier this year, reports showed the construction of dozens of new coal plants in China. In 2023, the country accounted for 95% of the construction of the world’s new coal power plants. There are a total of 1,142 operating coal-fired plants in China, which is five times more than in the U.S.
India, another major player in the Asian energy market, also saw an increase in coal imports and production. India has increased its spending on infrastructure, with an expected rebound in demand for coal-based steel and raw material manufacturing. Indonesia has 254 operational coal-fired power plants and 40 new plants under construction. Japan, too, is a big consumer of coal, being the top importer of Australian coal in recent years.
Like Australia, the U.S. has been a top source of coal imports for these Asian countries. S&P Global says, “U.S. metallurgical coal exports have seen growth fueled by Asian demand over the past few years. The potential for seaborne volumes to grow hinge on expansions in blast furnace steelmaking and met coke production in India, China, and Southeast Asia.” New mines such as Arch Resource’s Leer South and the AMCI, POSCO, and Itochu-led Allegheny Met’s Longview mine will play a role in meeting this demand from Asia.
Ironically, U.S. miners can meet Asian needs while their government rejects them as a fuel source for cheap electricity!
The advancement of recent emission-reduction targets for U.S. industry, as well as restrictions on the export capacity of natural gas by the Biden administration, is quite astonishing in light of the ongoing expansions in fossil fuel capacity by various Asian nations.
The quality of life for millions of Americans could very well decline in return for zero environmental benefits as that of Asians improves.
Vijay Jayaraj is a Research Associate at the CO2 Coalition, Arlington, Virginia. He holds a master’s degree in environmental sciences from the University of East Anglia, U.K.
This article was originally published by RealClearEnergy and made available via RealClearWire.