Table of Contents
Heather Shearer, Griffith University
Samuel Alexander, University of Melbourne

The reasons for choosing to go tiny range from reducing debt, inability to afford a conventional home, the search for sustainability, a life crisis, or even preparing for an uncertain future in the face of climate change by going off-grid. Or perhaps a combination of these.

An important first step is to decide what type of tiny house you want. To many, the phrase “tiny house” brings to mind an archetypal tiny house on wheels, a miniature cottage on a trailer, often made of wood, with a pitched roof and dormer windows.
Indeed, most tiny housers prefer some degree of mobility, whether a ready-made or DIY tiny house, converted caravan or bus/van. A survey by the Australian Tiny House Association found most (78% of 109 respondents) lived in tiny houses on wheels, but a small but growing proportion live in converted caravans, vans or buses.
Why do you want to go tiny?
First you need to evaluate your motives, which may differ according to your situation or stage of life. The most important question here is, how often do you want to move?
Do you want to be ultra-mobile, and live like a digital nomad, perhaps in a “stealth van” in the city, changing parking spaces every night? Or do you want to travel around Australia like a “grey nomad”, staying in caravan parks or roadside camps for a week or so before moving on?

Alternatively, do you want to be more settled, perhaps moving occasionally, to be closer to work, medical facilities or schools for children? (Yes, some tiny housers have children). Or do you want to travel between the houses of adult children or do petsitting, staying from weeks to months?
Many off-the-shelf caravans are extremely well designed and are accepted everywhere, at caravan parks or roadside parking areas. On the other hand, a tiny house on wheels is less mobile, and not suited to frequent moving (they are also extremely heavy, not aerodynamic and large tow vehicles are costly).

They’re also less accepted in caravan parks, and most local councils consider them caravans, with restricted periods of occupancy and often onerous conditions. Vans and buses are the most flexible (in the “stealth van” or vanlife movement, people live rent-free by parking, mostly illegally, often in industrial estates, and using public or work/gym bathrooms).
They are, however, extremely small and while it may seem glamorous to live in a van like celebrity rock climber Alex Honnold, the reality may not be practical.
What can you afford?
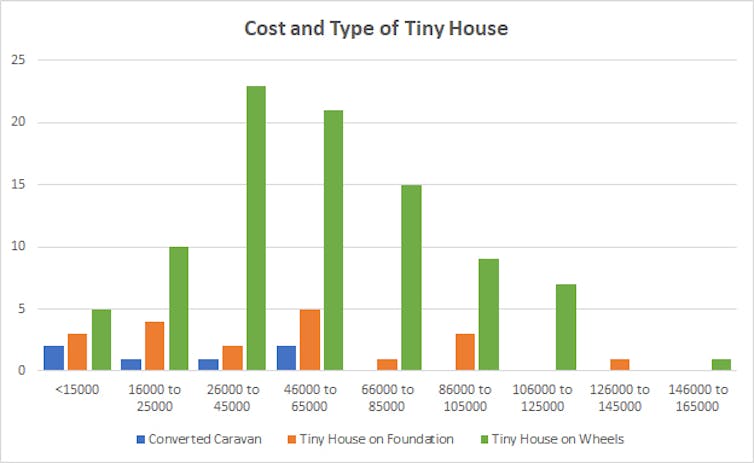
Cost will likely be the next factor to consider. Ready-built tiny houses range from around A$50,000 – $120,000; DIY are cheaper, especially if self-built, with some costing under $2,000. The higher end, architect-designed ones are more expensive.
Converted caravans can be affordable, even under $10,000, but prices vary markedly, with some ultra-luxurious five-wheelers costing more than a typical suburban house (>$600,000).
Converting old buses and vans is much cheaper, with the cost of the vehicle tending to be under $20,000. Of note, unless you are living under the radar or free camping, you are going to have to factor in the ongoing cost of renting someone’s backyard or caravan park space.
How sustainable is your choice?
Sustainability is a more nuanced aspect of tiny house living; living small means less energy needed for heating and less room for superfluous stuff, encouraging or enforcing a minimalist lifestyle.
Most tiny houses on wheels are off-grid to some extent, relying on solar power, rainwater and composting toilets. They are often built entirely out of sustainable or reclaimed materials.
On the other hand, most caravans and vans are not particularly sustainable — they’re often built out of mass-produced material and may produce outgassing from carpets and paints. Vans and busses are generally no more or less sustainable than any similar vehicle.
What kind of life do you want?
Tiny houses, whatever the type, are just that: tiny. Space is at a premium and living tiny requires reducing stuff, such as clothes, sporting and hobby equipment. Tiny houses on wheels, where parked more permanently, allow for decks and even sheds, but caravans and vans are self contained, unless in a permanent caravan park.
If you are used to living in a very large space, it may take time to adapt to the practicalities of tiny living; people often complain about cooking smells and composting toilets.
Despite the popularity of tiny houses however, very few people actually live in them. Nonetheless, the vast majority of people who live or have lived tiny, view their experience positively, and feel it has greatly enriched their lives, and helped them re-evaluate their life choices, especially consumerism even after moving to more conventional dwellings.
Heather Shearer, Research Fellow, Cities Research Institute, Griffith University and Samuel Alexander, Research fellow, Melbourne Sustainable Society Institute, University of Melbourne
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.