Table of Contents
As we are all confined to barracks, it is a great opportunity to try new things. How about a virtual tour of a world famous disaster site? No protective clothing is required. (Unlike a visit to your local supermarket.)
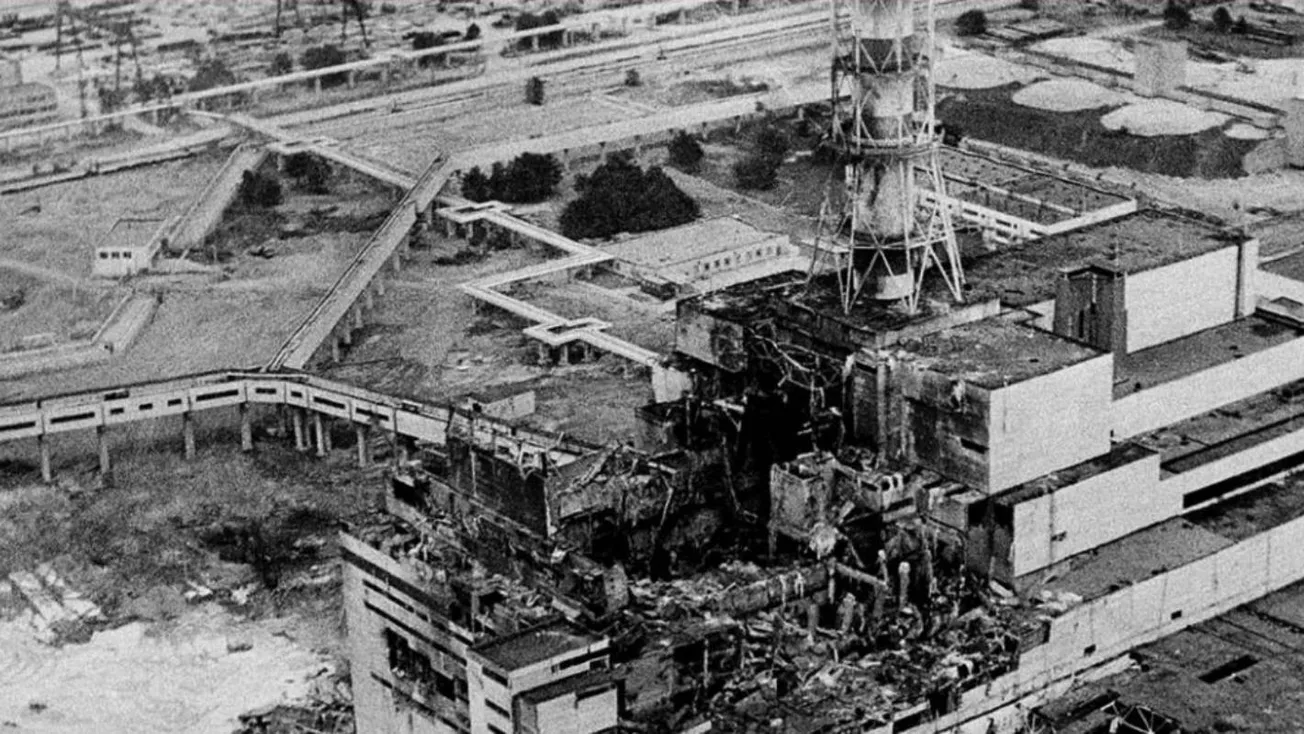
Today’s tour is of the Chernobyl Nuclear Plant. Wikipedia tells us:
The Chernobyl disaster was a nuclear accident that occurred on Saturday 26 April 1986, at the No. 4 nuclear reactor in the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant, near the city of Pripyat in the north of the Ukrainian SSR. It is considered the worst nuclear disaster in history and is one of only two nuclear energy disasters rated at seven—the maximum severity—on the International Nuclear Event Scale, the other being the 2011 Fukushima Daiichi nuclear disaster in Japan.
The accident started during a safety test on an RBMK-type nuclear reactor, which was commonly used throughout the Soviet Union. The test was a simulation of an electrical power outage to aid the development of a safety procedure for maintaining reactor cooling water circulation until the back-up electrical generators could provide power. This gap was about one minute and had been identified as a potential safety problem that could cause the nuclear reactor core to overheat. It was hoped to prove that the residual rotational energy in a turbine generator could provide enough power to cover the gap. Three such tests had been conducted since 1982, but they had failed to provide a solution. On this fourth attempt, an unexpected 10-hour delay meant that an unprepared operating shift was on duty. During the planned decrease of reactor power in preparation for the electrical test, the power unexpectedly dropped to a near-zero level. The operators were able to only partially restore the specified test power, which put the reactor in a potentially unstable condition. This risk was not made evident in the operating instructions, so the operators proceeded with the electrical test. Upon test completion, the operators triggered a reactor shutdown, but a combination of unstable conditions and reactor design flaws caused an uncontrolled nuclear chain reaction instead.
A large amount of energy was suddenly released, vapourising superheated cooling water and rupturing the reactor core in a highly destructive steam explosion. This was immediately followed by an open-air reactor core fire that released considerable airborne radioactive contamination for about nine days that precipitated onto parts of the USSR and western Europe, before being finally contained on 4 May 1986. The fire gradually released about the same amount of contamination as the initial explosion. As a result of rising ambient radiation levels off-site, a 10-kilometre (6.2 mi) radius exclusion zone was created 36 hours after the accident. About 49,000 people were evacuated from the area, primarily from Pripyat. The exclusion zone was later increased to 30 kilometres (19 mi) radius when a further 68,000 people were evacuated from the wider area.
Click on the door to see what’s revealed.