Table of Contents
Robert Kogon
Robert Kogon is a pen name for a widely-published financial journalist, a translator, and researcher working in Europe. Follow him at Twitter here. He writes at edv1694.substack.com.
Elon Musk’s announced “general amnesty” week has come and gone and there has been no sign of any amnesty at all. In particular, none of the – on Twitter’s own count – 11,230 accounts that have been suspended for violating the platform’s “Covid-19 misinformation” policy appear to have been restored.
Many have been wondering why the announced “amnesty” has not occurred. But the answer is obvious. The European Union vetoed it.
“The people have spoken. Amnesty begins next week. Vox Populi, Vox Dei,” Musk famously tweeted after an online poll he had posted resulted in a landslide in favour of “amnesty.” But the European Commission evidently believes in a different God.
Thus, on November 30, just two days after the amnesty was supposed to have gotten underway, the EU’s Internal Market Commissioner, Thierry Breton, posted an eerie 5-second clip on Twitter, showing a grim, stone-faced Musk on a video monitor being lectured by Breton, who is himself comfortably seated in a Brussels office on the backdrop of the EU flag.
I welcome @elonmusk‘s intent to get Twitter 2.0 ready for the #DSA??
— Thierry Breton (@ThierryBreton) November 30, 2022
Huge work ahead still — as Twitter will have to implement transparent user policies, significantly reinforce content moderation and tackle disinformation.
Looking forward to seeing progress in all these areas. pic.twitter.com/Nc7sGlb9YL
We cannot hear what Breton is telling Musk, since the clip has been posted without audio. The video conference appears to have taken place earlier on the same day.
The accompanying tweet reads: “I welcome @elonmusk‘s intent to get Twitter 2.0 ready for the #DSA Huge work ahead still — as Twitter will have to implement transparent user policies, significantly reinforce content moderation and tackle disinformation. Looking forward to seeing progress in all these areas.”
The “DSA” is the EU’s recently adopted Digital Services Act. As discussed in my earlier article here, the DSA threatens “very large” online platforms like Twitter with ruinous fines of up to 6 per cent of global turnover if they fail to comply with what the European Commission construes as their obligations under the EU’s so-called Code of Practice on Disinformation. The main focus of the “Code” for the last 2-plus years has been a “Fighting COVID-19 Disinformation Monitoring Programme,” which was instituted under it.
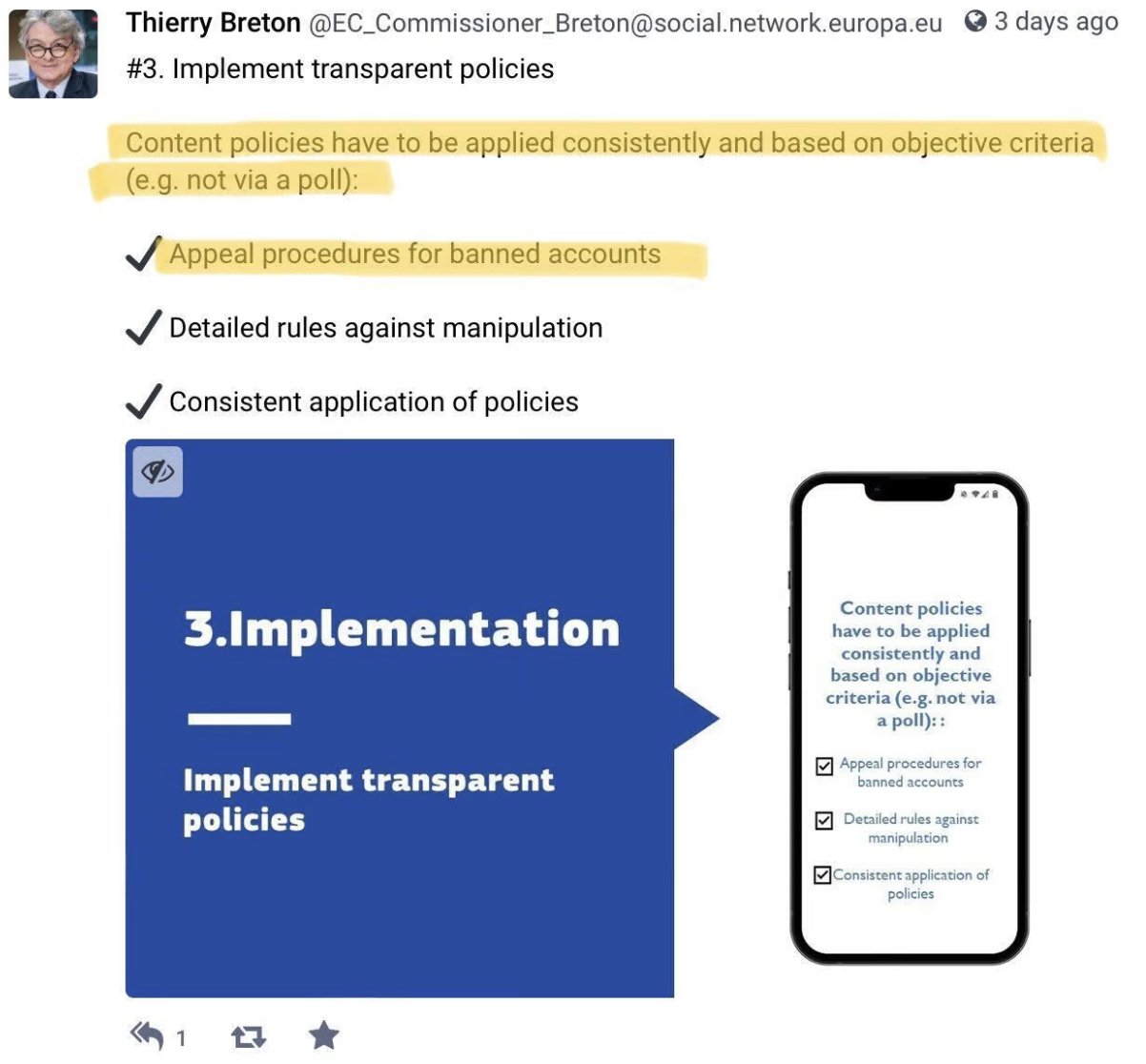
For further details on what exactly the EU Commission is demanding of Musk and Twitter to demonstrate compliance, Breton coyly links to a Mastodon thread containing a “DSA Checklist.” Item #3 (see below) amounts to a not-so-subtle reprimand of Musk for having proposed a general amnesty and, in particular, for having done so on the basis of the “Vox Populi, Vox Dei” principle. It calls merely for “appeal procedures for banned accounts” – i.e. no “amnesty,” whether general or partial – and insists: “Content policies have to be applied consistently and based on objective criteria (e.g. not via a poll).”
Item #1 demands that Musk and Twitter “reinforce content moderation” – aka censorship – and somehow, in the manner of squaring the circle, “protect freedom of speech” at the same time. Note that Breton’s tweet and the introductory post to his Mastodon thread both indeed call on Musk to “significantly reinforce content moderation,” thus making clear that the Commission not only disapproves of the prospect of banned accounts being restored but also of the relatively more laissez-faire attitude that Musk has thus far adopted toward current users.
But perhaps most tellingly, Breton’s introductory post notes his satisfaction at hearing that Musk “has read [the Digital Services Act] carefully” – highly unlikely given the length and complexity of the legislation – “and considers it as a sensible approach to implement on a worldwide basis.” The emphasis is mine.
This is to say that the EU’s censorship requirements are to be applied not only within the EU itself, but globally.
As discussed in my previous article, unbeknownst to most of the rest of the world, this is in fact what is happening, including in the United States, where any such legally-required abridgment of freedom of speech is obviously incompatible not only with the spirit, but also with the letter of the 1st Amendment.
Breton’s complete set of demands can be read here.