Table of Contents
Sonia Elijah
Sonia Elijah has a background in Economics. She’s a former BBC researcher and now works as an investigative journalist.
FDA loses its war on ivermectin and agrees to remove all social media posts and consumer directives regarding ivermectin and [Covid], including its most popular tweet in FDA history. This landmark case sets an important precedent in limiting FDA overreach into the doctor-patient relationship.
Dr. Mary Talley Bowden
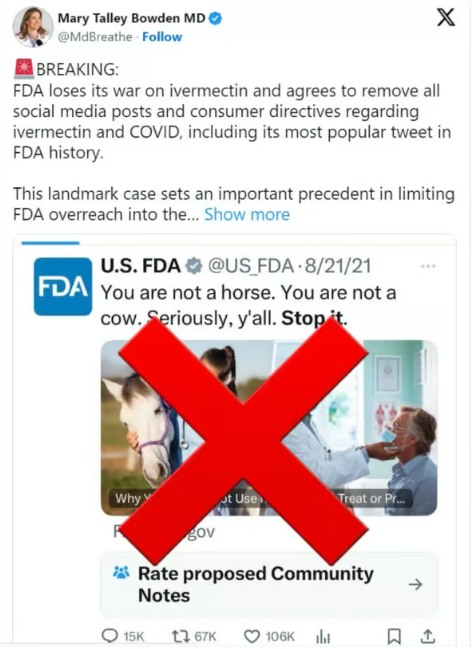
On March 21, a settlement was reached, leading to the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) agreeing to remove social media posts and webpages discouraging the use of ivermectin for treating Covid-19.
This landmark case was initiated by plaintiffs Drs. Mary Talley Bowden, Robert I. Apter, and Paul E. Marik, who filed a lawsuit against the agency under the leadership of Commissioner Robert Califf, MD. The lawsuit was prompted by the FDA’s dissemination of misleading information about ivermectin, a Nobel Prize-winning anti-parasitic drug with a long history of use and inclusion in the World Health Organization’s essential list of medicines.
An FDA spokesperson told the Epoch Times that the agency “has chosen to resolve this lawsuit rather than continuing to litigate over statements that are between two and nearly four years old.”
In light of the FDA’s unprecedented loss in their war against ivermectin, I thought it was fitting to bring to my readers’ attention my Trial Site News report from November 2021 on the agency’s “most successful” viral tweet, which can be read below.
FDA’s Smoking Gun: Disinformation Campaign Targeting Ivermectin
It recently came to my attention that communication within the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) evidences the Gold Standard agency’s explicit involvement in the Ivermectin disinformation war. While the agency approves ivermectin as an anti-parasite medicine, physicians have increasingly embraced it as an off-label treatment for early-onset Covid-19. Over 60 studies around the world have, for the most part, found positive findings; however, the mainstream media embraced the handful that are neutral or had data problems, for example. Regardless of position, a disinformation campaign was initiated by the FDA and others to deter the use of the off-label treatment. See the email here.
In my investigative report about how ivermectin became a target for the ‘fraud detectives,’ published in TrialSite, I highlighted the relentless smear campaign against this life-saving generic drug by a certain group of scientists/bloggers, which has been amplified in the mainstream media. My report included the overtly biased and controversial ‘You’re not a horse’ tweeted by the FDA. However, the revelatory email communication within the FDA exposes the insidious nature of this government agency’s deep involvement as one of the major planners of this disinformation war against ivermectin.
The definition of disinformation is:
‘Deliberately misleading information announced publicly or leaked by a government or especially by an intelligence agency in order to influence public opinion or the government in another nation.’
Conflating Veterinary and Human Versions
Secured via Freedom of Information Act (FOIA) request by investigative reporter Linda Bonvie, the email involves esteemed members of the world’s top regulatory body bragging and boasting about how many tweets the “You’re not a horse” tweet did with engagement.
Showcasing the agency’s front and central role in promoting propaganda, the author, Erica Jefferson, an associate commissioner for the FDA’s external affairs, boasts to Dr. Janet Woodcock, the FDA’s acting commissioner, how the “Not a Horse Tweet” got 14.5 million tweets. (See below)
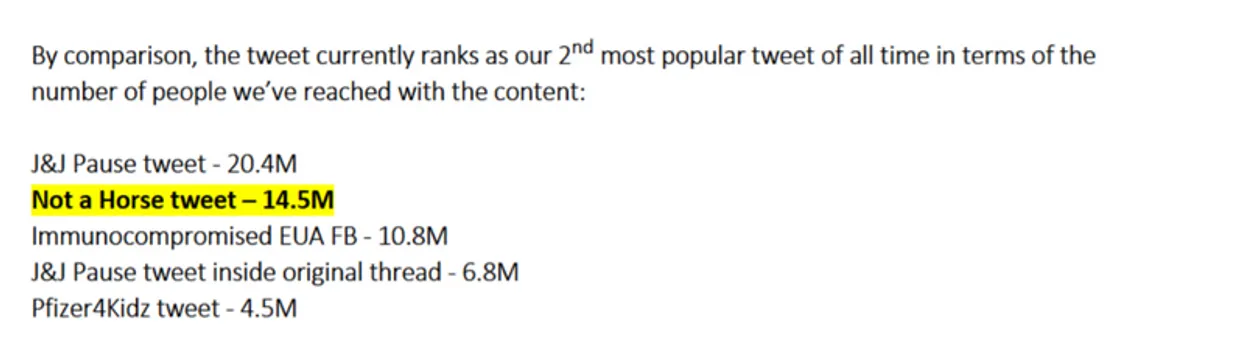
Jefferson expresses her excitement of the ‘FDA ivermectin/[Covid]-19 tweet’ going viral. She writes, ‘needless to say the straightforward and clever (humourous) communication…saw the tweet quickly going viral and being shared across multiple social medium platforms (where it was amplified by other influencers) and resulted in additional news coverage by: NYT, CNN, NBC News and Rolling Stone to name but a few.’
FDA as Social Media Manipulator
Jefferson’s reference to ‘other influencers’ on social media amplifying the message and helping it go viral is very revealing, including the role of mainstream media. It can be said that this speaks to a larger network of entities involved in the disinformation campaign against ivermectin- like the Trusted News Initiative, a consortium of Big Tech (Twitter, Facebook, Microsoft) and Big Media set up to combat anti-vaccine ‘disinformation’ and from what is becoming evidently clear, early-treatments for Covid-19, too.
The tweet posted by the FDA (see below) was published on August 21, 2021, with the email from Erickson to Woodstock sent the following day. Copied in were many high-ranking FDA officials, such as Julia Tierney, acting chief of staff, Melissa Safford, senior advisor to the commissioner.

FDA Purposely Creating Confusion Among Consumers
Yes, a version of ivermectin is used for veterinary purposes, but the massive increase in prescriptions that concerned the FDA was the human variety, prescribed by licensed physicians with consent from their patients. But the messaging was meant to confuse people to think that they were one and the same. Of course, those people who were involved with self-medication needed education, but what the FDA does here is try to kill two birds with one stone. The FDA doesn’t go out of its way to educate but instead spread disinformation.
Jefferson reveals in her email that the Office of External Affairs (OEA) team had spent ‘the past several weeks’ planning in how to effectively use their social media platforms ‘to share important public health information.’ She references the news coming out of Mississippi regarding the use of ivermectin to treat Covid-19 ‘and the increase in adverse events (poisonings).’
It seems the FDA seized the opportunity in the Mississippi State Department of Health’s network alert sent out on August 20 stating that ‘70% of the recent calls have been related to the ingestion of livestock formulations of ivermectin.’ This is confirmed in her email, as Jefferson writes, ‘I’m sure you saw some of the news coming out of Mississippi on Friday night [August 20]…I expressed to the team late Friday night that we take the opportunity to remind the public of our warnings for ivermectin…’
What is very alarming is not only the level the FDA has stooped to in planning and executing a smear campaign against ivermectin, but the fact that the ‘poisonings’ could be based on inaccurate data.
Nonetheless, the mainstream media jumped on the ‘poisonings’ bandwagon, citing the Mississippi department of health data. The Guardian ran with the headline, ‘A human is not a horse. So why is a livestock drug sweeping America?’ However, the department later clarified it was only 2% of calls that were made to the state’s poison control centre that related to the ingestion of animal formulations of ivermectin, not 70%.
The Rolling Stone (which turned out to be a fraudulent piece), the New York Times, Washington Post, Associated Press, and indeed, the Guardian all had to print corrections regarding the false information.
Both the CDC and FDA also pointed to data from the Association of Poison Control Centers (AAPCC) that purported to show a three-fold increase in calls involving ivermectin. TrialSite secured that data and found that the number of calls went from 435 to 1,143, and the overwhelming number of them were harmless. TrialSite disclosed that 11 of the calls, or about 1%, involved a serious matter. However, it’s not clear if they were associated with any hospitalization.
TrialSite found that at least by September, there were no deaths from ivermectin—although since then, there have been a few reported. Billions of doses of ivermectin have been administered by the Mectizan program, evidencing an extraordinary safety record. Of course, self-medication without physician oversight with any drug is wrong. Still, the FDA’s social media engagement sought to appropriately dissuade the veterinary variety’s use while inappropriately confusing the consumer by making them think all of the medication is for animals.
Why Wouldn’t the FDA Also Share the Truth With Consumers?
Over 60 studies have produced some overwhelmingly positive data points for ivermectin. While the FDA and others have discounted many of those studies, the drug is used by several countries as an emergency use authorized treatment—albeit in mostly low-income countries. But the important studies demonstrated potential, including the ICON case series study in America.
The National Institutes of Health now sponsors ACTIV-6, a major clinical trial involving ivermectin. Led by Duke Clinical Research Institute, this is clear evidence that the government has enough interest in the drug to at least invest (finally) to evaluate. Although, some advisors of TrialSite have suggested the study is underdosed. The University of Minnesota, along with UnitedHealthcare, also funds an ivermectin study called Covid-Out.
Why didn’t the FDA take the time to educate the public about this and instead ‘create a unique viral moment?’ Why just the singular message that served to conflate the illicit use with legitimate use by licensed physicians and consenting patients?
Regulatory agencies should be educating people not engaging in social medial disinformation campaigns. It was this same message that was used, for example, by CNN. TrialSite covered that interview on the Joe Rogan Show where Sanjay Gupta called this kind of tactic done by the FDA as “snarky.”
If this is how the FDA hopes to ‘reach the “everyday” American to “brand” FDA’ with a disinformation campaign targeting this life-saving drug, then the American public is in deep trouble, and so are the rest of us.
Republished from the author’s Substack